Patient with acute pain at the bottom of the back in general practice. Diagnosis of the fracture of the lower limb. Collecting anamnesis, examination of brain concussion
■ Neurological picture interpretation and subjectivism.
■ Figure is neurological symptoms.
■ The predominance of general-selling symptoms over focal.
■ lack of meningeal symptoms in young children with subarachnoid hemorrhages.
■ Relative rarity intracranial hematomas.
■ Frequent development of the head of the brain.
■ Good regression of neurological symptoms.
The closed TBI includes the concussion of the brain, the brain injury is light, medium and heavy degrees and compression of the brain, which is often celebrated against the background of his bruise. The reason for the compression of the brain is most often an intracranial hematoma, less commonly - fragments of the skull with the so-called revealed fracture.
The diagnosis of CMT is based on the identification of the following signs.
■ The fact of the head of the head or the head in history.
■ Visually defined damage to the soft tissues of the head, the bones of the skull.
■ Visually defined signs of the fracture of the base of the skull.
■ Violation of consciousness and memory.
■ Symptoms of lesion of cranial nerves.
■ Signs of focal brain lesions.
■ Oolate listening symptoms.
Violation of consciousness. With a lot of CMT (concussing the brain or his injury injury), the loss of consciousness in preschool children is rare. Currently adopted the following gradation of violations of consciousness.
■ Clear consciousness: The child is fully oriented, adequate and active.
■ Moderate stun: A child in consciousness, partially oriented, answers questions rather correctly, but reluctantly and monosyllant, drone.
■ Pronounced stun: A child in consciousness, but his eyes are closed, disoriented, only answers simple questions, and not immediately, only after repeated requests, performs simple commands, drone.
■ Sopor: Child unconscious, eyes closed. Reacts only to pain and eye opening; However, contact with patients cannot be installed. Well localizes pain: it cuts the limb at injection, protected. Dominance flexible movements in the limbs.
■ Moderate coma: a child unconscious - "non-trae", the pain reacts with a common reaction (it shudders, shows anxiety), but does not localize pain, does not protect. Vital functions are stable, with good parameters.
■ Deep coma: A child unconscious - "Failing", does not react to pain. Muscular hypotension. Dominates the tone of the extensors.
■ Exchangeable coma: a child without consciousness - "non-disgrace", does not respond to pain. Sometimes it makes spontaneous extension movements. Muscular hypotension and areflexia. Vital functions are rudely broken: no self-breathing, pressure 70 mm Hg. and below.
Memory Disorders Memory Disorder are celebrated from victims with a medium and heavy degree of gravity of brain bruises, in children with a long loss of consciousness. If the child does not remember the events that occurred before the injury, they state retrograde amnesia, after injury - anterograd amnesia.
Headache occurs almost all of all victims, with the exception of children under 2 years old. The pain is diffuse and with light injury is not painful, pokes alone.
Vomiting, like a headache, arises almost all of all victims, but if it is, as a rule, it is, as a rule, with heavy - repeated.
Symptoms of defeat of the cranial nerves
■ Violation of the innervation of pupils: the lethargy of the reaction to light, with a heavy CMT - its absence, pupils can be evenly expanded or narrowed, an aisocorium may indicate a brain dislocation at an intracranial hematoma or a heavy basal injury.
■ Deviation of the language, asymmetry of the face when grilled, ockering. The persistent asymmetry of the face indicates a medium-sized or severe CMT.
Reflexes and muscular tone. Rogped reflexes are either declined or disappeared. Muscular tone changeable: from moderate hypotension with light injury until the tone increases in the height of the body and limbs with heavy.
Pulse frequency and body temperature. The pulse frequency can vary in large limits. Bradycardia testifies to progressive intracranial hypertension - hematoma brain squeezing.
Features of the Diagnostics of CHMT in children of the first year of life. The acute period is characterized by a short-term, predominance of general-selling symptoms, and sometimes the absence of general-selling and focal symptoms. Basic symptoms for diagnosis:
■ Piercing Creek or short apnea at the time of injury;
■ The emergence of motor automatics (sucking, chewing, etc.);
■ Jumping or vomiting;
■ Vegetative disorders (hyperhydrosis, tachycardia, fever);
Diagnostics of the severity of CMT
■ concussion brain.
Short-term loss of consciousness (up to 10 minutes). If there was more than 15 minutes from the moment of injury before the arrival of the SMP brigade, then the child is already in consciousness.
Retrograde, less often Anterograd amnesia.
Vomiting (more often 1-2 times).
Lack of focal symptoms.
■ brain injury (for the diagnosis is enough to have one characteristic).
The loss of consciousness is more than 30 minutes or a violation of consciousness at the time of inspection, if the term from the moment of injury until the brigade arrival is less than 30 minutes.
The presence of focal symptoms.
Visible fractures of the bones of the skull.
Suspicion of the fracture of the skull base (symptom of "points", Likvorea or hemolycower).
■ Ground brain compression.
The compression of the brain, as a rule, is combined with his injury. The main reasons for the compression of the brain are intracranial hematomas, revealed fractures of the bones of the skull, the head of the brain, subdural hygromas.
Main clinical symptoms of brain compression - limb paresis (contralateral hemipapes), anisocorium (gomolateral meydriasis), Brass. It is characteristic of the presence of a "light" gap - improving the state of the child after injury, followed by deterioration. The duration of "light" gap - from a few minutes to several days.
We are carried out with brain tumors, hydrocephalus, the aneurysms of the brain vessels, inflammatory diseases of the brain and its shells, poisoning, commen during diabetes mellitus.
■ control over the ABC system; Start hydrochyotherapy (60-100% oxygen), the imposition of the neck collar with suspected injury of the cervical spine.
■ with deep and proven coma - tracheal intubation after intravenous administration of 0.1% atropine solution 0.1 ml / year, but not more than 1 ml.
■ IVL at a deep coma in cases of signs of hypoxemia.
■ With a coordinated coma - IVL in moderate hyperventilation mode.
■ Correction of decompensation of hemodynamics of infusion therapy with a decrease in systolic blood pressure below 60 mm Hg. (See the section "Infusion therapy at the prehospital stage").
■ Prevention and treatment of brain edema are carried out when the diagnosis of the brain's injury is established. Dexamethasone is introduced 0.6-0.7 mg / kg or prednisone 5 mg / kg intravenously or intramuscularly (only in the absence of arterial hypertension). Furosemid in a dose
1 mg / kg intravenously or intramuscularly administered only in the absence of arterial hypotension and data indicating the compression of the brain.
■ if the victims of the convulsive syndrome, psychomotor excitation, hyperthermia, etc.
■ Hemostatic therapy: ethanzite (dicinone *) 1-2 ml intravenously or intramuscularly.
■ For anesthesia, if necessary, apply drugs that do not depress the respiratory center (tramadol - 2-3 mg / kg intravenous, sodium metamizole (analgin *) - 50% solution of 0.1 ml / year intravenously). Preparations that depress the respiratory center (narcotic analgesics) can be administered with the mandatory IVL [Trimpeleridine (processed *) - 0.1 ml / year intravenously].
■ All symptoms in children with CMT are distinguished by inconsistency, which necessitates careful observation. Therefore, all children with suspicion of the THMT, even if there is only an anamnestic indication of injury without clinical manifestations, are subject to mandatory hospitalization in a hospital with neurosurgical and resuscitation offices.
Brain-brain injury
Card-brain injury - damage to the bones of the skull and / or soft tissues (brain shells, brain fabrics, nerves, vessels). By the nature of the injury distinguish the closed and open, penetrating and impermealing CMT, as well as concussion or brain injury. The clinical picture of the cranial and brain injury depends on its character and severity. The main symptoms are headache, dizziness, nausea and vomiting, loss of consciousness, memory violation. The brain injury and intracerene hematomas are accompanied by focal symptoms. The diagnosis of the cranial injury includes anamnestic data, neurological inspection, skull radiography, CT or MRI brain.
Brain-brain injury
Card-brain injury - damage to the bones of the skull and / or soft tissues (brain shells, brain fabrics, nerves, vessels). The CMT classification is based on its biomechanics, the form, type, character, form, gravity of damage, clinical phase, treatment period, and the outcome of the injury.
By biomechanics distinguish the following types of CMT:
- shock-shockproof (the shock wave applies to the place of the resulting strike and passes through the brain to the opposite side with rapid pressure drops);
- acceleration-deceleration (moving and rotation of large hemispheres in relation to a more fixed brain barrel);
- combined (the simultaneous impact of both mechanisms).
By type of damage:
- focal (characterized by local macrostructural damage to the brainstant, with the exception of sections of destruction, finely and large-scale hemorrhages in the field of impact, anti-dust and shock wave);
- diffuse (tension and distribution by primary and secondary bumps of axons in the seven-board center, cornistal body, subcortical formations, brain trunk);
- combined (combination of focal and diffuse brain damage).
According to the genesis of the defeat:
- primary lesions: focal bruises and brain scratch, diffuse axonal damage, primary intracranial hematomas, trunk breaks, multiple intracerebral hemorrhages;
- secondary lesions:
- due to secondary intracranial factors (delayed hematomas, disorders of liquor and hemocirculation due to intraventric and subarachnoid hemorrhage, brain edema, hyperemia, etc.);
- due to secondary extra charge factors (arterial hypertension, hyperkapinia, hypoxemia, anemia, etc.)
According to its type, CMT are classified on: closed - damage, not disturbing the integrity of the skin of the head; fractures of the bones of the skull of the skull without damage to the adjacent soft tissues or the fracture of the base of the skull with the developed leafores and bleeding (from the ear or nose); An open imperimental CMT - without damage to the solid cerebral shell and the open penetrating CMT - with damage to the solid cerebral shell. In addition, isolated (absence of any extra charge damage), combined (extra charge damage resulting from mechanical energy) and combined (simultaneous effects of different energies: mechanical and thermal / radial / chemical) cranial injury.
By gravity, the THMT is divided by 3 degrees: light, medium gravity and heavy. With the correlation of this heading with the scale coma of Glasgow, the light cranial and brain injuries are estimated at 13-15, medium-stroke - in 9-12, heavy - in 8 points and less. A lightweight brain injury corresponds to a shaking and a brain's ears of a lightweight, medium-heavy - the injuries of the medium brain, heavy - the injury of a severe brain, diffuse axoneal damage and acute brain squeezing.
According to the mechanism of the occurrence of CMT, the primary (effect on the brain of traumatic mechanical energy does not precede any cerebral or extrasebral catastrophe) and the secondary (the effects of traumatic mechanical energy on the brain is preceded by a cerebral or extrasebral catastrophe). CMT in the same patient may occur for the first time or re-(twice, three times).
The following clinical forms of CMT are distinguished: concussion of the brain, a brain injury to an easy degree, an in-degree brain injury, a severe brain injury, diffuse axonal damage, compression of the brain. The flow of each of them is divided into 3 basic periods: acute, intermediate and remote. The temporal length of the periods of the flow of the cranial and brain injury varies depending on the clinical form of the CHMT: acute - 2-10 weeks, intermediate - 2-6 months, remote under clinical recovery - up to 2 years.
Brain concussion
The most common injury among possible cranial brain (up to 80% of all CHMT).
Clinical picture
The oppression of consciousness (to the spin level) when the brain is concussion, it can continue from a few seconds to a few minutes, but maybe there is no absent. For a short period of time, retrograde, cunning and antegradine amnesia develop. Immediately after the crank-brain injury, a single vomiting arises, breathing is expensive, but soon comes back to normal. It also comes to normal and blood pressure, with the exception of those cases when the history is burdened by hypertension. The body temperature when concussing the brain is kept normally. When the victim comes into consciousness, there are complaints about dizziness, headache, general weakness, the appearance of cold sweat, tides blood to face, noise in the ears. The neurological status at this stage is characterized by a soft asymmetry of skin and tendon reflexes, a fine horizontal nistagm in the extreme leads of the eyes, light meningial symptoms that disappear during the first week. When concussing the brain as a result of the cranial injury after 1.5 - 2 weeks, an improvement in the general condition of the patient is noted. It is possible to preserve some asthenic phenomena.
Diagnosis
The recognition of the concussion of the brain is a difficult task for a neurologist or traumatologist, as the main criteria for its diagnosis are components of subjective symptoms in the absence of any objective data. It is necessary to familiarize yourself with the circumstances of the injury, using the information available in the witnesses of the incident. Of great importance is the survey of a spinner, with which they determine the presence of symptoms of irritation of the vestibular analyzer in the absence of signs of loss. Due to the soft semiotics of the concussion and the possibility of a similar picture as a result of one of the many dotraumatic pathologies, the dynamics of clinical symptoms is attached to the dynamics of clinical symptoms. The rationale for the diagnosis of the "concussion" is the disappearance of such symptoms after 3-6 days after receiving the cranial injury. When concussing the brain there are no fractures of the bones of the skull. The composition of the liquid and its pressure is maintained. At CT of the brain, intracranial spaces are not defined.
Treatment
If the victim with the cranial trauma came to himself, first of all he needed to give a comfortable horizontal position, the head should be slightly raised. The victim with the cranial and brain injury, which is unconscious, must be given. The "saving" position is to put it on the right side, the face must be turned to the ground, the left hand and the leg bent at right angles in the elbow and the knee joints (if the spinal fractures and limbs are excluded). Such a position contributes to the free passage of air into the lungs, preventing the spares of the tongue, the fall of the vomit, saliva and blood in the respiratory tract. On bleeding wounds on the head, if any, impose a aseptic dressing.
All those affected with the cranial injury are mandatory transported to the hospital, where, after confirmation, the diagnosis establishes them by bed per term, which depends on the clinical features of the course of the disease. The absence of signs of focal brain lesions on CT and MRI brain, as well as a patient's condition, allowing to refrain from active drug treatment, make it possible to resolve the issue in favor of the patient's extract for outpatient treatment.
With a concussion of the brain, excessive drug treatment does not apply. Its main goals is the normalization of the functional state of the brain, the relief of headaches, normalization of sleep. For this, analgesics are used, sedatives (usually tableted forms).
Brain injury
The injury of the brain of a light degree is detected in 10-15% of victims of the cranial trauma. The injury of height is diagnosed in 8-10% of victims, heavy injury - in 5-7% of victims.
Clinical picture
For the brain's injury, the loss of consciousness is characterized after an injury to several dozen minutes. After the restoration of consciousness, complaints appear on headache, dizziness, nausea. Remarks retrograde, conung, anterograd amnesia. Vomiting is possible, sometimes with repetitions. Vital functions are usually preserved. Moderate tachycardia or bradycardia is observed, sometimes an increase in blood pressure. Body temperature and breathing without significant deviations. Mildly pronounced neurological symptoms are regressed in 2-3 weeks.
The loss of consciousness when the brain injury to the middle degree can be fed to 5-7 hours. The retrograde, cunning and anterograde amnesia is strongly expressed. Multiple vomiting and severe headache is possible. Some vital functions are violated. Bradycardia or tachycardia is determined, an increase in blood pressure, tachipne without a respiratory impairment, an increase in body temperature to subfebrile. Perhaps the manifestation of shell signs, as well as stem symptoms: bilateral pyramidal signs, nystagm, dissociation of meningeal symptoms along the axis of the body. Pronounced focal signs: eye-minded and pupil disorders, parish limbs, speech disorders and sensitivity. They are regressed in 4-5 weeks.
The injury of the brain of severe is accompanied by a loss of consciousness from several hours to 1-2 weeks. Often it is combined with fractures of the bones of the base and the skull vessel, abundant subarachnoid hemorrhage. Disorders of vital functions are noted: a violation of the respiratory rhythm, a sharply increased (sometimes reduced) pressure, tachy-or bradyritium. Possible blocking of the airways, intense hyperthermia. The focal symptoms of the lesion of the hemispheres are often disguised as a stem symptom (nystagm, parires, dysphagia, ptosis, mydriasis, decending rigidity, a change in tendral reflexes, the appearance of pathological stop reflexes). Symptoms of oral automatism, paresay, focal or generalized epiprigances can be determined. Restoring lost functions is hard. In most cases, coarse residual motor disorders and mental disorders are preserved.
Diagnosis
The method of choice in the diagnosis of brain injury is CT brain. A limited zone of reduced density is determined on CT, fractures of the bones of the skull, subarachnoid hemorrhage are possible. When the brain injury to the medium severity on CT or spiral CT, in most cases, focal changes are detected (noncompact zones of reduced density with small areas of high density).
When a severe injury injury on CT, zones of inhomogeneous increase in density (alternation of areas of increased and reduced density) are determined. Perifocal brain edema is greatly expressed. A hypodenzystic path is formed into the area of \u200b\u200bthe nearest department of the side ventricle. Through it, fluid is discharged with products of blood decomposition and brain tissue.
Diffuse axonal brain damage
For diffuse axonal brain damage, a typical long-term comatose state after a cranial injury, as well as pronounced stem symptoms. The coma is accompanied by symmetric or asymmetric decependence or decortication of both spontaneous and easily provoked irritations (for example, pain). Changes in muscle tone are very variable (hydrogen simony or diffuse hypotension). Typically, the manifestation of pyramid-extrapyramidal passage limbs, including asymmetric tetrapreza. In addition to gross rhythm violations and respiration, vegetative disorders appear: an increase in body temperature and blood pressure, hyperhydrosis, etc. The characteristic feature of the clinical course of diffuse axonal brain damage is the transformation of the patient's condition from the long coma to the transient vegetative state. The spontaneous opening of the eyes shows the occurrence of such a state (there are no signs of tracking and fixing the gaze).
Diagnosis
The CT-picture of the diffuse axonial lesion of the brain is characterized by an increase in the volume of the brain, as a result of which the side and III ventricles are under compression, subarachnoid convexital spaces, as well as brain base tanks. Often, the presence of small-scale hemorrhages in the white substance of the hemispheres of the brain, the corn body, subcortical and stem structures.
Brain compression
The brain compression is developing in more than 55% of cases of cranial injury. Most often, intracranial hematoma (intracerene, epi or subdural) becomes the cause of the brain. The danger to the life of the victim is rapidly growing focal, stem and communal symptoms. The presence and duration of the T.N. "Light gap" - unfolded or erased - depends on the severity of the condition of the victim.
Diagnosis
The CT is determined by a two-way, less often flat-convex limited zone of increased density, which adjoins the tile of the skull and is localized within one or two fractions. However, if there are several bleeding sources, an increased density zone may be a significant size and have a sickle form.
Cerebral injury treatment
Upon admission to the intensive care unit, the patient with the cranial and brain injury it is necessary to carry out the following activities:
- Inspection of the body of the victim, during which they detect either exclude abrasions, bruises, deformities of the joints, changes in the form of the abdomen and chest, blood and / or course of ears and nose, bleeding from the rectum and / or urethra, the specific smell of mouth.
- Comprehensive X-ray examination: skull in 2 projections, cervical, chest and lumbar spine, chest, pelvic bones, upper and lower extremities.
- Ultrasound of chest, ultrasound of the abdominal cavity and retroperitoneal space.
- Laboratory studies: general clinical analysis of blood and urine, biochemical blood test (creatinine, urea, bilirubin, etc.), blood sugar, electrolytes. These laboratory studies must be carried out in the future, daily.
- ECG (three standard and six breasts).
- Study of urine and blood for the content of alcohol. If necessary, consult a toxicologist.
- Consultation of neurosurgeon, surgeon, traumatologist.
A compulsory method of examination of victims with ancient brain injury is a computed tomography. Relative contraindications to its conduct are hemorrhagic or traumatic shock, as well as unstable hemodynamics. With the help of CT, the pathological center and its location, the number and volume of hyper-and hyperial zones, the position and the degree of displacement of the middle structures of the brain, condition and the degree of damage to the brain and the skull are determined. With suspected meningitis, it shows the carrying out of a likvore, which allows you to monitor changes in an inflammatory character.
The neurological examination of the patient with the cranial and brain injury should be carried out every 4 hours. To determine the degree of violation of consciousness, the scale of the Coma Glasgow (speech condition, the response to the pain and the ability to open / close the eyes) is used. In addition, they determine the level of focal, eye-minded, pupil and bulbar disorders.
The victim with a violation of the consciousness of 8 points and the less on the scale of Glasgow shows the intubation of the trachea, due to which the normal oxygenation is supported. The oppression of consciousness to the level of the coporn or coma is an indication to carry out an auxiliary or controlled IVL (at least 50% oxygen). With its help, optimal cerebral oxygenation is supported. Patients with severe acceleracy injury (identified on CT hematoma, brain swelling, etc.) need to monitor intracranial pressure, which must be maintained at a level below 20 mm Hg. For this purpose, mannitol, hyperventilation, sometimes barbiturates are prescribed. For the prevention of septic complications, escalation or de eager antibacterial therapy is used. For the treatment of post-traumatic meningitis, modern antimicrobial drugs are used, allowed for endolumbal administration (Vancomycin).
Patient nutrition starts no later than 3 three days after CMT. Its volume increases gradually and at the end of the first week, which has passed since the acquisition of the cranial and brain injury, it must provide 100% caloric need for the patient. Method of power can be enteral or parenteral. For the relief of epileptic attacks, anticonvulsant preparations are prescribed with minimal dose titration (levethiracets, hollows).
Indication to the operation serves epidural hematoma with a volume of more than 30 cm³. It has been proven that the method that ensures the most complete hematoma evacuation is transcranial removal. Acute subdural hematoma with a thickness of more than 10 mm is also subject to surgical treatment. Patients in a coma remove the sharp subdural hematoma with craniotomy, while maintaining or removing bone flap. Epidural hematoma volume of more than 25 cm³ is also subject to compulsory surgical treatment.
Forecast during brain injury
The concussion of the brain is predominantly reversible clinical shape of the cranial injury. Therefore, in more than 90% of the cases of brain concussion, the outcome of the disease becomes the recovery of the victim with the full restoration of working capacity. In part of the patients, after an acute period of concussion, they note those or other manifestations of post-commercial syndrome: disruption of cognitive functions, mood, physical well-being and behavior. In 5-12 months after the cranial injury, these symptoms disappear or are smoothed substantially.
The prognostic assessment in severe acceleracy injury is carried out using the Glasgow Exodus scale. A decrease in the total number of scores on the Glasgow scale increases the likelihood of unfavorable outcome of the disease. Analyzing the prognostic significance of the age factor, it is possible to conclude its substantial impact on both disability and mortality. The combination of hypoxia and arterial hypertension is an unfavorable factor of the forecast.
Card and brain injury - treatment in Moscow
Manager of Diseases
Nervous diseases
Latest news
- © 2018 "Beauty and Medicine"
it is intended only for familiarization
and does not replace qualified medical care.
CMT in history
The frequency of the cranial injury is constantly increasing, primarily due to the growth of road traffic accidents. In economically developed countries, the incidence is approximately 8,000 cases on the I million of the population per year, of which at about half of the victims requires hospitalization. Approximately 2.5-5% of patients need subsequent rehabilitation.
Depending on gravity distinguish the following types of brain injuries:
The injury of soft tissues of the head without damaging the brain (including in the absence of signs of concussion of the brain); In such cases, treatment is usually required,
Concussion of the brain (may be accompanied by a fracture of the bones of the skull),
Brain injury (not always accompanied by a fracture of the bones of the skull and in exceptional cases can flow without brain concussions),
Penetrating injury: open direct damage to the brain substance, always accompanied by a fracture of the bones of the skull,
Early and late complications of the cranial and brain injury, in particular the compression of the brain.
The clear boundaries between the bruise of soft tissues of the head and the concussion of the brain, as well as between the shaking and the brain injury, is not always easy. The presence or absence of a fracture of the skull bones is not a criterion for the severity of damage to the brain itself.
When finding out the circumstances, injury should pay special attention to:
Current time, view and direction of damaging impact,
Head security at the time of injury (for example, the presence of a headdress),
Memories of the patient himself about that. how the injury happened,
The presence and duration of retrograde amnesia (events that occurred immediately before injury),
The duration of the admirograd amnesia (events that occurred after the injury)
The presence of nausea and vomiting.
When examining a patient with a "fresh" cranial and brain injury, special attention must be paid to the following:
External damage, especially in the head area
The expiration of blood or the CSZH from the nose, ears, zea,
Damage to the cervical spine,
The presence of periorubital hematoma (symptom of "points") and / or a rings of euricular hematoma,
General condition, especially the condition of the cardiovascular system (the development of shock is possible), neurological status (the state of pupils, vision, hearing, the presence of nystagma, parares, pyramid signs),
In patients in an unconscious state, the X-ray of the cervical spine is obligatory.
Conducting the skull radiography: the exclusion of intracranial hemorrhage exclusion may require neurovalization methods (preferably CT). CT head, spent around after injury, often releasing a greater amount of damage than in the first hours. Using MRI, you can diagnose in-fatenitorial damage. In addition, on T2-weighted MRI images you can identify signs of diffuse axonial damage ("ringing injury"), most often in the area of \u200b\u200bthe corpulent body and in the subcortical white substance of the frontal fraction.
Materials are prepared and posted by visitors to the site. None of the materials can be applied in practice without consulting the attending physician.
Materials for placement are accepted on the specified mailing address. The site administration retains the right to change any of the assigned and placed articles, including complete deletion from the project.
0027 Open brain injury.
Main tabs
- Surname, name, patient patient:
- Age: 25 years
- Gender: Male
- Place of work and position:
- Home address:
- Date of receipt in the clinic: 11/13/06, 13 22
- Date of statement:
- Diagnosis at hospitalization: open cranial trauma. Brain injury.
- Diagnosis Clinical: open cranial trauma. Fracture of the base of the skull on the right. Brain injury. Post travematic neuritis facial nerve on the right.
- Related diseases: no
- Complications: No.
Upon admission and at the time of the corporation, the patient makes complaints on moderate stitching constant pain in the right-hand temporal area, increasing when taking a vertical and semi-propical position, which are boring by the intake of analgesics; On the constant omission of the right upper eyelid, the right corner of the mouth, the weakness of the mimic muscles on the right, the decline in hearing on the right ear.
Anamnesis of the present disease
He was injured on 10.20.06 as a result of a road accident: in a state of intoxication was shot down by a passenger car. Events at the time of injury and within 24 hours after it does not remember. During this time, it was delivered to the CRH, where the diagnosis was made: "Open skull-brain injury: a fracture of the base of the skull on the right, a stupid trauma of the abdomen", splectomy produced. The emergence of complaints on headaches, a decrease in the rumor to the right - since the recovery of consciousness, about 1 week after injury, the patient noted the appearance and gradual increase in the asymmetry of the face and weakness of the mimic muscles on the right. The essential dynamics of these complaints in connection with treatment in the CRH (drugs are difficult to call it difficult) was not observed, which was the reason for the direction of the patient to the neurosurgical department of the Zaporizhia Regional Clinical Hospital.
Anamnesis of life without features.
Objective condition of the patient
The condition of the patient of the middle gravity, the situation is active, the consciousness is clear. The physique is hyperstenic proportional.
Head of ordinary shape and sizes.
Skin covers pale, moderately wet, with numerous scars, incl. And on the skin of the head, visible mucousse without features. Gorgeous, ear, submandibular, rear, front-first, permissible, subclavian, axillary, elbow, popliteal lymph nodes are not palpable.
Cardiovascular system: when inspection and palpation without peculiarities, with percussion of the border of cardiac stupidity within the normal range. Auscultative tones of hearts are clear, no noise. Pulse satisfactory filling and voltage.
Respiratory system: breathing through the nose is free. In case of inspection and palpation, the chest without singularities, with percussion over the entire surface of the lungs, a clear pulmonary sound is listened. Auscultation over the entire surface of the lungs breathing vesicular, there are no wheezes.
The system of digestion organs: on the front abdominal wall - the postoperative scar of the white lines of the abdomen. When palpation is a soft, soreness in the course of the intestine is not determined. Chair is normal. The size of the liver in the crusure - 9 * 8 * 6 cm.
Hell 125/80 mm Hg.st.
Pulse 78 per minute.
The frequency of respiratory movements is 18 per minute.
Notes permanent headache in the right temporal area. Episode of Ante and Retrograde Amnesia due to injury and operational intervention.
The study of the cranial brain nerves: VII steam. When examining the face - the omission of the right upper eyelid, the right nasolabial fold and the right corner of the mouth. Raise and frowning eyebrows, the eye clogging is weakened on the right, on the leftmost. At the request of smiling, show your teeth marked a significant decrease in the volume of movements of the mimic muscles on the right.
There is a decline in rumor to the right ear.
Data of additional examination methods
Displacement M-ech. Uneven intracranial hypertension.
11/15/06. Study of electrical conductivity.
Right facial nerve at the II current I, II, III centuries -
on P-current I, II, III centuries - reduced
contracture for II c.
11/15/06. Inspection of the eyepiece
Visod \u003d 1,0, Visos \u003d 0.2 (low since childhood)
13.11.06. MRI brain
CONCLUSION: injury of the crust departments of the left frontal-temporal area.
Based on the complaints, anamnesis, data objective and additional examination of the patient, you can formulate a clinical diagnosis:
Open cranopy and brain injury. Fracture of the base of the skull on the right. Brain injury. Post travematic neuritis facial nerve on the right.
"Open cranopy and brain injury": justified by an indication of an accident on an accident, written confirmed information about the examination in the CRH (given the prescription of the onset of the disease), the presence of scars on the skin of the head, the development of the clinical painting of the brain's injury.
"The fracture of the base of the skull on the right" is justified by an indication of an accident on an accident, in writing confirmed information on the survey in the CRH (given the prescription of the onset of the disease).
"The brain injury" is substantiated by an indication of a history of accidents, documented information about the fracture of the skull bones, the formation of a resistant focal symptomatomy (local headache, a decrease in rumor on the right) immediately after injury, data of the echeg of survey on the displacement of Mr., MRI conclusion brain.
"The post-trap neuritis face nerve right" is justified by the above data on the fracture of the bone of the skull, in the channels of which passes the facial nerve, complaints and data of the neurological examination on the weakness of the mimic muscles on the right, the study of the electrical conductivity of the right face nerve.
With all the brain injuries, bed and complete peace are prescribed for 5-6 days in easy cases and for up to several weeks in heavier. You can put a cold compress on my head. When bleeding from the nose or ears can not be resorted to washing and tight tamponade, sterile dressings should be applied.
The presence of lycvorea creates a risk of infection of the brain. In these cases, an intensive antibiotic therapy is prescribed. To stop bleeding are prescribed inside calcium chloride (10% solution of 1 tea or tablespoon 3 times a day). With a falling of cardiac activity, camphor, caffeine, Cordiamine (age doses), are prescribed, with breathing disorders - lobeline (1 ml of 1% solution), cytifyon (0.5-1 ml intramuscularly), inhalation of oxygen with carbon dioxide. Conduct a fight against edema and swelling of the brain with the help of dehydrating agents: intramuscularly 1-3 ml of a 25% solution of Magnesia sulfur (daily), intravenously 40% glucose solution, and for every 10 ml 1 drop of 3% of the ephedrine solution, prednisone is added. Saluratets (Furosemid in a dose of 0.5-1 mg / kg per day) are prescribed in the first day after injury (at the same time Panangin, orotat or potassium chloride) are administered to prevent hypokalemia). In the development of a clinical picture of increasing intracranial hypertension, dislocations and brain comprehension due to its edema, osmotic diuretics (mannitis, glycerin) are used at a dose of 0.25-1 g / kg. Repeated or long-term use of saluretics and osmotic diuretics is possible in conditions of careful control over the state of the water and electrolyte balance. To improve the venous outflow from the cavity of the skull and reduce intracranial pressure, it is advisable to put the patient to the position with a raised head. Subsequently, it is possible to prescribe a background-Rig - 0.04 g / kg (daily dose).
In cases of psychomotor arousal, convulsive reactions use sedative and anticonvulsant preparations (Sibazon, barbiturates, etc.). When shock, the elimination of pain reactions is needed, the replenishment of the shortage of circulating blood volume, etc. (see traumatic shock). Conducting therapeutic and diagnostic manipulations, including patients in a coma, should be carried out under conditions of blockade of pain reactions, since they cause an increase in volumetric blood flow and intracranial pressure.
In cases where the above methods do not eliminate intracranial hypertension, persistent convulsive and severe vegal-visual reactions, and the results of clinical and instrumental studies make it possible to eliminate the presence of intracranial hematomas, barbiturates or sodium oxybutirate are used against the background of artificial ventilation of the lungs with careful control. intracranial and blood pressure. As one of the methods of treatment of intracranial hypertension and brain edema, a dosage discharge of the cerebrospinal fluid was used using the catheterization of the side ventricles of the brain.
With severe bruises and brallos of the brain with its expressed swelling, antimemental drugs are used - inhibitors of proteases (conficilla, farm, etc.). It is also advisable to use inhibitors of peroxidation oxidation of lipids antioxidants (tocopherol acetate, etc.). With severe and medium-wing brain injury, vasoactive preparations are used - Eufillin, Cavinton, Sermion, and others. Intensive therapy also includes maintaining metabolic processes using enteral (probe) and parenteral nutrition, correction of disorders of acid-alkaline and water-electrolyte balance, Normalization of osmotic and colloidal pressure, hemostasis, microcirculation systems, thermoregulation, prevention and treatment of inflammatory and trophic complications. In order to normalize and restore the functional activity of the brain, nootropic drugs (piracetam, aminalon, pyridaltal, etc.) are prescribed, funds normalizing the exchange of neurotransmitters (Galanamine, Leveodop, Nakom, Madopar, etc.).
Events for care for patients with cranial trauma include the prevention of laying hypostatic pneumonia (frequent turning of the patient, banks, massage, skin toilet, etc.), passive gymnastics to prevent the formation of contractures in the joints of the parethous limbs. In patients in the state of a copor or coma, with a violation of swallowing, a decrease in cough reflex must be monitored by the loss of respiratory tract and with the help of a suction to release the oral cavity from saliva or mucus, and during intubation of the trachea or tracheostomy to sanitize the lumen of the tracheobronchial tree. Carry out control over physiological poisoning. Take measures to protect the cornea from drying (hardening in the eyes of vaseline oil, the closure of the age with the help of the leukoplasty, etc.). Regularly spend the toilet of the oral cavity.
It is resorted to lumbacal puncture only with pronounced phenomena of intracranial hypertension and with coarse stem symptoms. It should not be released during puncture more than 5 ml of cerebrospinal fluid due to the risk of penetrating the cerebellum into a large occipital hole. If there is blood (subarachnoid hemorrhage), daily punctures with the release of 3-5 ml of cerebrospinal fluid are shown. A decrease in brain edema also contributes to the purpose of 0.015-0.03 g of diphrol in powder 2-3 times a day and 0.1-0.15 ml of 0.1% atropine solution subcutaneously.
With an open cranial injury and the development of infectious inflammatory complications, antibiotics are prescribed, well penetrating through the hemat andintephalic barrier (semi-synthetic analogs of penicillin, cephalosporins, leftomycetin, aminoglycosides, etc.). The ribbon-bruised wounds of the soft coverings of the skull penetrating deeper by the aponeurosis require primary surgical treatment and mandatory prevention of the tetanus (a tetanus anatoxine is introduced, anticipating serum).
The optimal deadlines for primary surgical processing from the moment of injury. In some cases, the initial surgical treatment of wounds with the imposition of deaf seams on the third day after injury is carried out. The primary surgical treatment of wounds of the skulls is produced under local anesthesia 0.25-0.5% novocaine solution. Hair on the head in the circumference of the wound shake. The thrown, the uneven edges of the wound are excised on the thickness of the thickness, retreat from the edge of 0.3-0.5 cm. In doubtful cases, instead of applying seams, the wound drain. Locally, antibiotics can be applied to the wound in a dry form.
Resuscitation measures in severe brain injury are starting at the pre-hospital stage and continue under the hospital. In order to normalize respiration, provide free permeability of the upper respiratory tract (release them from blood, mucus, the masses, the administration of the duct, the flow of the trachea, tracheostomy), use the inhalation of the oxygen-air mixture, and, if necessary, performed artificial ventilation of the lungs.
The forecast for recovery is unfavorable, since the brain injury is accompanied by the formation of a focal macromorphological defect of the brain substance, which is why the full regression of focal symptoms is impossible.
The forecast for life can be considered favorable because the period when the likelihood of the development of hazardous complications is highest, already passed, and the vital centers of the brain are not damaged. Forecast for working capacity is favorable, but is required to transfer to another job, not related to significant physical and psycho-emotional loads.
This patient as transferred to the cranial and brain injury is subject to long-term dispensary observation. According to the testimony, regenerative treatment is carried out. Along with the methods of therapeutic physical education, physiotherapy and work therapy, it is necessary to use metabolic (piracetam, aminalon, pyriditol, etc.), vasoactive (Cavinton, Sermion, Cinnarizin, etc.), anticonvulsant (phenobarbital, leshes, diphenin, pantogam, etc.), Vitamin (B1, B6, B15, C, E, etc.) and resorbing (aloe, vitreous body, fibs, lidase, etc.) preparations.
In order to prevent epileptic seizures, often developing in patients after ancient brain injury, this patient should assign drugs containing phenobarbital. It is shown for a long time (within 1-2 years) a single reception at night. Therapy is selected individually taking into account the nature and frequency of epileptic paroxysms, their dynamics of age, premorbide and the overall state of the patient.
To normalize the overall functional state of the CNS and accelerate the recovery tempo, vasoactive (Cavinton, Sermion, Cinnarizin, Ksantinol Nicothet et al.) And nootropic (piracetam, pyridaltal, aminal, etc.) drugs that should be combined, assigning them alternating two-month courses ( At intervals of 1-2 months.) For 2-3 years. This basic therapy is advisable to supplement the means affecting the tissue exchange; amino acids (cerebrolysin, glutamic acid, etc.), biogenic stimulants (aloe, vitreous body, etc.), enzymes (lidase, lectures, etc.). In case of violations of the psyche for observation and treatment of the patient, a psychiatrist is attracted.
Catad_Tema Back Pain - Articles
Patient with acute pain at the bottom of the back in general practice
Pain at the bottom of the back (BNCC) is an extremely common symptom with which neurologists, therapists and family doctors face almost daily.
Depending on the duration of the BNCC, it is divided into acute, subacute and chronic. BNCC is considered acute if 6 weeks last or less, subacute - if 6-12 weeks lasts. Chronic pain lasts more than 12 weeks. Depending on the duration of the pain, it is possible to assume a forecast: 60% of patients with acute BNCC are returned to work within a month, 90% for 3 months.
Causes of BNCCs are different. For convenience, they are accepted to be grouping in 3 categories: potentially hazardous diseases, Ishialygia and nonspecific pain symptoms caused by mechanical reasons.
Potentially dangerous diseases
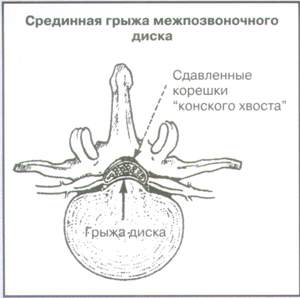
This group includes tumors, infections, spinal injuries, as well as "horse-tail" syndrome. It is possible to suspect them during the collection of anamnesis and physical examination (Table 1). With these diseases, immediate additions are required.
Ishialia
The pain during Ishiagia is keen in the leg and corresponds to the innervation zone of the compressed root or nerve. Sometimes pain is localized only in the leg. Most often suffer the roots of L5 and S1 (Fig. 1). Ishialyg is often accompanied by extremely pronounced pain syndrome, but in most cases it passes with conservative therapy. Sometimes the operational treatment is shown.
Nonspecific back pain caused by mechanical reasons
Some patients note pain localized in back, not related to root symptoms or any serious diseases. This category includes mechanical BNCC. Improving the condition of the patient is achieved with conservative treatment.
The basis of the differential diagnosis is to collect anamnesis and physical research.
Anamnesis
Diagnostics in BNCC requires careful analysis of the history. Mechanical causes of acute BNCCs cause dysfunction of muscular and skeletal structures and a ligament. Pain may proceed from the tissues of the intervertebral disc, joints and muscles. The forecast in pain of mechanical origin is usually favorable.
Secondary pain requires the search and treatment of the main disease. Secondary pain occurs much less often than pain caused by mechanical causes. Secondary BNCC can be suspected of people under 20 and over 50 years old. Clinical symptoms contributing to the diagnosis are listed in Table. 1. More rare causes of secondary acute BNCCs, which are not included in the table, are metabolic bone damage, reflected by the pain of the BRI of the diseases of the abdominal cavity organs, the retroperitoneal space and the pelvis, the disease of the Pedge, Fibromyalgia, psychogenic pain.
Anxiety symptoms that should alert the doctor and require further examination, are listed in Table 2.
Physical research
Gait and posture
The assessment of the gait and posture is necessary in all patients with complaints about BCCS. Scoliosis can be functional, but may also indicate muscle spasm or neurogenic disorders.
With damage to the root L5 there are difficulties when walking on the dogs, with damage to the root S1 - on socks.
Volume of movements
It should be evaluated how the patient makes tilts forward, extension, slopes of the lobby and the rotation of the upper half of the body. Pain with inclined forward is observed more often and is usually associated with mechanical reasons. If the pain occurs when the spine is extension, it is possible to consider the possibility of a spinal stenosis channel (Fig. 2). Unfortunately, the assessment of the volume of movements has a limited diagnostic value, although it is useful for assessing the effectiveness of treatment.
Palpation and percussion of the spine
Palpation pain and percussion of spinal spinal processes may indicate the presence of a fracture or vertebral infection. Palpation of the paravertebral space allows you to outline the painful zones and reveal muscle spasm.
Walking "heel-sock" and a sample with squats
The inability to overture from the heel on the sock or to make squats is characteristic of horse-tail syndrome and other neurological disorders.
Palpation of sedlicate clipping
Painting in the palpation of a sedlicated cutting with irradiation in the leg indicates irritation of the sedinese nerve.
Samples with raising straightened legs (provocative samples)
The patient lies on his back, the doctor raises his straightened leg on the side of the defeat. You should estimate the angle of lifting legs. The appearance of pain in the range of 30-60o indicates a positive symptom of Lasega. Flexion of legs in the knee joint should reduce the pain, and the compression of the popliteal area is to strengthen it. Pressing on the knee joint straightened and raised legs with the simultaneous rear flexion of the foot will also lead to an increase in pain.
The sample with a straight line gives a positive result in 95% of patients with a disk hernia; However, it is also positive and in 80-90% of patients who do not find any signs of disk protrusion on operations. Another sample - with a raising straight leg, opposite to the side of the lesion (the same as in the previous test, is considered positive when pain occurs) is less sensitive, but much more specific to the diagnosis of the hernia disk.
Reflexes, muscle strength and sensitivity
The study of knee and ankle (achillovy) reflexes in patients with root symptoms often helps a topical diagnosis.
Achilles Reflex loosens (drops) with the hernia of the L5-S1 disk. With the hernia disk L4-L5, tendral reflesses on the legs do not fall out. The weakening of the knee reflex is possible with the radiculopathy L4 root in the elderly patients with the stenosis of the spine canal. Disk hernia at the L3-L4 level are very rare.
Weakness at the extension of the thumb and foot indicates the involvement of the root L5 (Fig. 4). For damage to the root S1, paresis of the calf muscle is characteristic (the patient cannot walk on socks).
Evaluation of the sensitivity of the skin of the leg and foot (Fig. 4) also allows you to estimate the level of the lesion. S1 radiculopathy causes hyptetic over the rear surface of the tibia and the outer edge of the foot. The squeezing of the root L5 leads to the hypsheat of the back surface of the foot, thumb and the interfallated interval.
Fast neurological examination
In case of primary treatment of a patient with BNCC and root symptoms, a neurological examination may be limited to only by several tests: assessment of the strength of rebar / extension of the foot and thumbs (as an option - walking on socks and heels), knee and achilla reflexes, check sensitivity of the foot and leg, as well as the lasheg breakdown. Such an abbreviated examination makes it possible to identify clinically significant radiculopathy associated with the hernia disk of the lumbar spine. If in a month the improvement does not occur, it is necessary to further examine or send to a specialist. When progressing symptoms, the examination must be carried out immediately.
Fig. one.
Reisants of the spinal cord root compression at the lumbar spine
 |
 |
Table 1.
Causes of BNCH
|
Diseases |
Keys to the diagnosis |
|
Nonspecific BNCH, caused by mechanical causes: diseases and damage to the bone-articular and muscular-ligament |
Pain is localized in the lumbosacral region, no root symptoms |
|
Ishiagniya (more often the hernia of the L4-L5 and L5-S1 disk) |
The root symptoms from the lower extremities, a positive test with a raising of the straightened leg (reception of Lasega) |
|
Spinal fracture (compression fracture) |
Previous injury, osteoporosis |
|
Sponddylis (splitting the body of the overlying vertebra, more often at the level of L5-S1 |
Physical exercise and sports are frequent provoking factors; Pain intensifies when the back is extension; X-ray in oblique projection reveals a defect of the intermediate part of the arms of the vertebra |
|
Malignant diseases (myeloma disease), metastase |
Inexplicable body weight loss, fever, changes in the electrophoresis of serum proteins, malignant diseases in history |
|
Connective tissue diseases |
Fever, increase ESP, antinuclear antibodies, scleroderma, rheumatoid artitis |
|
Infections (disc, tuberculosis and osteomyelitis spine, epidural abscess) |
Fever, the introduction of preparations of parenteral, tuberculosis in history or positive tuberculin test |
|
Aortic abdominal aneurysm |
The patient is moving, pains do not decrease alone, pulsating weight in the stomach |
|
Syndrome "horse-tail" (tumor, median hernia disk, hemorrhage, abscess. Tumor |
Urine delay, urine incontinence or feces, saddot anesthesia, pronounced and progressive weakness of lower extremities |
|
Hyperparathyroidism |
Gradual start, hypercalcemia, kidney stones, constipation |
|
Ankylosing spondylitis |
In most cases, men of the 3rd decades of life, morning stiffness, positive HLA-B27 antigen, increase |
|
Nephrolithiasis |
Color pain in the side departments with irradiation in groin, hematuria, the inability to find a comfortable position of the body |
Fig. 2.
Nature of the spine canal

Due to the expanding of osteophytes, the channel acquired the characteristic form of a tribal. In this case, the compression of both a separate root and the roots of the horse-tail leads to mono or polyradiculopathy. Often, a pseudo-performing chromotype occurs during the stenosis of the spine channel: pain in the lumbar-sacral region (perhaps in the buttocks and legs) appears during walking and passes when the patient sits down.
Table 2.
Anxiety symptoms with acute BNCC
Anamnesis Physical examination |
Table 3.
Indications for radiography during acute BNCC
Fig. 3.
Sadlovoid anesthesia

Saddle-like anesthesia is often a manifestation of a horse-tail syndrome, which in addition to anesthesia may include: bilateral stylish, sudden appearance of a delay or incontinence of urine, incontinence of feces, lower sludge parapaprez.
Fig. four.
Symptoms of damage to roots L4-S1
Table 4.
Waddel criteria
Inadequate reaction |
|
|
Surability |
Surface (with insignificant pressure) and inappropriate anatomical structures |
|
Simulation |
Vertical load on the standing patient's head causes BNCC |
|
Passive rotation of the shoulder belt and pelvis in the same plane causes BNCC |
|
|
Non-compliance with symptoms |
The discrepancy between the symptoms when conducting a sample with a lift of the straightened leg in the sitting position and lying |
|
Regional disorders |
|
|
Muscular weakness |
According to the type "gear" |
|
Sensitivity |
Loss of sensitivity not suitable dermatome |
|
Excessive patient reaction |
Excessive grimacing, spelling or tremor during examination |
Laboratory tests
As a rule, at the initial stages of examination of patients with acute BNCC, laboratory research is not needed. If the tumor suspected or the infectious process requires a general blood test and ESR. Other blood studies are recommended only if any primary disease is suspected, for example, ankylosing spondylitis or a faith (analysis on HLA-B27 and serum protein electrophoresis, respectively). When suspicion of the pathology of urinary tract, a general analysis of urine is shown.
To identify metabolic diseases of bones, calcium levels, phosphates and alkaline phosphatase activity are determined.
X-ray study
Indications for the radiographic study during acute BNChs are listed in Table. 3.
Rengeniography of the spine to all patients with BNCH does not make sense, since certain changes can be detected from almost all patients. On the regenogram of the patient, there are no complaints on the back pain in the back of the back (osteochondrosis, deforming osteoarthritis, sacralization or lumbalization of the vertebrae). On the contrary, a patient with BCCs changes can be minimal.
If there is a horse-tail syndrome or a progressive muscular weakness, a computer tomography, magnetic resonance imaging, myelography is shown. Conducting these studies is also suitable in preparation for surgical intervention.
Treatment
Most patients with acute BNCCs show only symptomatic treatment. At the same time, about 60% of patients note the improvement during the first 7 days of treatment and the overwhelming majority - for 4 weeks. Patients should be instructed that in case of deterioration of motor or sensory functions, pain enhanced, the appearance of disorders of the functions of the pelvic authorities, they should immediately consult a doctor again to continue the survey.
As pain decreases, patients should be gradually returned to normal operation. It is shown that maintaining activity within the limits that makes pain contributes to a more rapid recovery than bedding or immobilization of the lumbar department.
Patients with such pathology help moderate physical exercises with minimal load on the back.
Drugs used in acute BNCC include non-steroidal anti-inflammatory agents (NSAIDs) and paracetamol. It is also possible to use muscle relaxants. It is shown that patients taking opioid analgesics return to normal activity no faster than host NSAIDs or paracetamol. Mioryelaxants have a greater anesthetic effect than placebo, but do not have the advantages over NSAIDs. Oral glucocorticoids and antidepressants do not have an effect in such patients, and their application is not recommended.
Currently, new drugs affect directly at the spinal cord level, which avoids a plurality of undesirable phenomena characteristic of the groups listed above. The first representative of the new class of substrates of electoral activators of the volatile channels of neuron (SNEPCO \u003d Selective Neuronal Potassium Channel Opener) is flipirtin
I.. It has a combination of painful and muscle relaxing properties, which is especially important in the treatment of pains of the musculoskeletal system and muscle spasms.
The greatest effect of flospirtin should be expected with pain syndromes whose pathogenesis is a mirror reflection of the properties of the drug. Considering that it possesses both an anesthetic and a myarlaxing effect, then these are sharp and chronic diseases in which pain is caused by muscle spasm, especially the pain of the musculoskeletal system (neck and back), muscle spasms for diseases of the joints.
In contrast to traditionally used painkillers (NSAIDs, opioid analgesics, muscle relaxants), it does not inhibit cyclooxygenase, does not have an opioid and generallylable action and, therefore, free of side effects inherent in these substances.
In several randomized studies, the effectiveness of manual therapy is demonstrated. Some patients may be useful in the shoes of special ralk or supinators. But exercises on the "stretching" of the spine, percutaneous electrostimulation, injection into trigger points or into intervertebral joints and acupuncture usually do not effect. Some patients who have conservative therapy does not give effect and limiting the activity of symptoms remain a month of treatment, surgical treatment can be shown.
Patients who already have the symptoms listed in Table at the first appeal to the doctor. 2, need soon turn-out and qualified treatment.
Diagnostic complexity with acute BNCH Literature:
Sometimes complaints about acute BNCCs are due to inorganic reasons. Psychosocial reasons may be economic (for example, an increase in financial compensation during disability) or social (dissatisfaction with the work) of character. In the event that there is a suspicion of psychosocial factors, the doctor may ask the patient to note on the figure depicting the human body, the spread of pain. If the distribution of pain does not correspond to anatomical benchmarks, psychogenicity is highly sounded. There is also a waddel criteria complex (Table 4), which can be easily carried out during normal physical research. G. Waddel noted that most patients with the BCCs organic origin of these criteria are not either detected only one criterion. If the patient has three and more WADDEL criteria, with a great degree of confidence, you can talk about psychogenic BNCC or simulation.
Bratton R.L. ASSESSMENT AND MANAGEMENT OF ACUTE LOW Back Pain. American Family Physician, 1999; 60 (8): 2299-2306.
Material prepared by R.I. Elagin, Cand. honey. science
Department of Clinical Pharmacology MMA. THEM. Sechenov
Catadolon® - Dossier drug
2. Anamnesis of damage
As with any damage to the musculoskeletal system, finding out the injury mechanism is important and should always be preceded by a clinical examination of the patient and the conduct of radiological research. It is necessary to try to determine the position of the foot at the time of injury and the direction of the stress (traumatic) effect of force, as well as clarify all other data that allow you to recreate the most likely damage mechanism. It is also useful to find out whether any crunch was at the time of injury, which may indicate a bundle, sublit or dislocation or a tendon displacement. In addition, it is necessary to find out the dynamics of the development of pain (i.e. the doctor should ask the victim if the appearance of pain was sudden or she gradually increased, whether his swelling appeared immediately after injury) and disabled timing (i.e. it was delayed or immediate ). Anamnesis should contain information about the preceding damage to the ankle joint and their treatment.
3. Clinical examination
Clinical examination of the patient should always precede X-ray research. If the contours of the ankle joint are deformed and the unstability of the joint is obvious, then the x-ray study must be fulfilled only after the doctor is taken in the absence of innervation violations of the affected area. In the absence of pronounced deformation of the joint, the prevalence of swelling of soft tissues is estimated, and subcutaneous hematomas are detected, which may indicate the presence of a fracture or damage to the ligaments. During palpation, the region of maximum pain, attitation and disappearance or change (displacement) of anatomical landmarks is determined.
It is necessary to estimate the volume of movements in the damaged joint and determine the positions of the foot, in which the pain is enhanced or weakens. Manipulations should be done very carefully to avoid additional damage. After the study of the damaged joint, it is necessary to assess the amount of possible movements in the normal skunk joint of another leg for comparison. At the same time, again, the existing anamnestic data on previous damage should be taken into account.
X-ray study
Radiography allows you to reveal fractures and determine the degree of gravity. Radiographs of the area of \u200b\u200bdamage allow to make an indirect conclusion about possible injuries of ligaments and tendons, as well as establish the presence of foreign bodies and diseases of the bone, which matters to prevent complications. Finally, the doctor can use X-ray pictures to assess the results of treatment.
Important in the study of any damage to the ankle joint has the right choice of projections. It is necessary to obtain the following X-rays: in the front-length of the projection when the foot is given by 5-15 °; in lateral projection with the inclusion of the base of the fifth tie bone; In oblique (internal) projection at an angle of 45 ° at the rear bending of the ankle joint. Radiographs in all indicated projections should be quite high-quality, which will allow to evaluate the trabecular structure of bones. For a comparative study, it is advisable to obtain a snapshot of the intact joint of another leg, especially in children. To accurately determine the contours of small bones and detecting swelling of soft tissues, the doctor must use a powerful lamp (bright light).
4. Damage to the borders of the ankle joint
Configuration breaks are approximately 75% of all damage in the field of ankle joint. More than 90% of cases are damaged outdoor ligaments; the share of injuries of the deltoid ligament accounts for less than 5%; With the same frequency (5%), the front or rear interbetous bunch, as well as the front and rear capsule departments, are damaged. Among the damage to the outer ligaments, 90% is the ruptures of the anterior tranny-small-terroral bundle (65% of them are isolated, and 25% are combined with damage to the heating-mulberry bundle). The rear taranno-small bunch (or the third component of the outer collateral ligament) is resistant to the displacement of the tone of the boost and, therefore, rarely damaged, except for the cases of full, dislocation of the foot. Since the anterior tranny-small-terror and heating-mulberry bundles are two separate structures, the standard classification of damage to the first, second and third degree here is unlikely to be applicable. Therefore, the injury of these ligaments is determined either as damage to one bundle, or as damage to both of them. When only one of these bundles occurs, only one-sided violation of the integrity of the joint occurs, which optionally leads to its instability. These bundles usually burst in a certain sequence - in front of the back, so the front taranno-small-metal bunch is first bursting, and then the heal and mulberry.
Damage to the anterior tranny-small-terror bunch
The weakness of this bundle can be fully appreciated with an objective study. At the same time, the most appropriate test with the extension of the foot forward. If the bundle is damaged, then such a nomination leads to anterior outer submission of the tank of the tone of the joint with apparent deformation and attitudes when limiting the foot excursion. This reception is performed in all patients with suspected damage to side ligaments.
One hand is captured by a foot per heel, placing a large and index fingers behind the ankles, and the other - stabilize the appointment department of the leg in the lower third. It produces easy-to-flexure of the foot and its turn of Knutrice, which is the normal position of its relaxation. Then they guide the knob's stop, while holding the shin in a fixed position. The displacement of the pork of the dice is more than 3 mm can be considered significant; The displacement of more than 1 cm is definitely significant. When testing, both false-positive and false-negative results are noted, but the greatest difficulties are due to the lack of acquaintance of the doctor with the procedure for conducting this study.
If the gap is propagated by the stopper on the heel-mining part of the side ligament, then a certain rone of the tanny is observed.
If the rupture applies to the stop-up to the heel-small-cell part of the side bundle, then a certain tap of the tank is observed, since the side department of the ankle joint is now becoming unstable not only in the frontroad plane, but also medial-lateral. This can be installed by attaching to the foot, the position of the plantar bending by 20-30 ° with a slight conversion and checking the tilt or the movement of the tunny bone relative to the distal part of the joint surface of the tibia. Then this is compared with normal mobility on the other side.
To properly assess the state of the ligaments, good muscle relaxation is important. If the diagnostic methods are performed cause pain, then the emerging (free or unwitting) protective abbreviation of muscles prevents the study. It is advisable to use ice or local infiltration anesthetic.
In case of damage to the rear taranno-mulobersoy bunch, the unstable of the ankle joint is obvious: positive signs when testing with the displacement of the foot of the Kepent and a noticeable roll of the tanny. With most damage to this bundle, there is a dislocation of ankle joint, so the need for any tests does not occur.
Damage to the internal collateral bundle
Isolated damage to the internal collateral ligament is rarely observed. Its injury is usually combined with a fracture of a small-terror bone or a breakdown of interbecamic syndesmosis. Such damage is most often the result of the forced conveying of the foot of the bed. The condition of the internal collateral ligament is estimated at the deviation of the foot in the direction from the inside of the dust.
Damage to interbecoval syndesmosis
Interbetal ligaments are a continuation of interceptional ligaments in the distal part of the tibial and small -com bones. Damage to this bundle system occurs due to excessive rear flexion and turning the foot. The tank bone is usually pushed up up, inclusion between the beam bones and shifting the small bone of the duck, which leads to a partial or complete break of the syndesmosis. Diastases are not always determined on radiographs or when examining the patient, since the inter-emergency membrane above the syndesmosis usually holds the tibial and low-tech bones together.
Anamnesis is often without peculiarities, however, patients are reported that at the time of injury they had a feeling of some kind of click on the back of flexion and turning the foot. There are insignificant swelling, as well as pain in the front and the aspour of the ankle joints. The patient prefers walking with a support on the fingers of the foot. During the examination, a painful point over the front or rear bundles is detected. Some soreness can be determined in the medial part of the ankle, which is due to the accompanying damage to the internal collateral ligament. With severe damage, tension in the distal part of the Mulobers and Tibraly bones is also determined. In addition, bilateral alignment of the ankle causes pain, as well as some movement in the damaged area. X-ray changes can reflect only swelling of soft tissues in the field of the medial part of the ankle (or above it) and above the lateral part of the ankle to the middle of the diaphysis of the mulberry bone. This is very serious damage with significant remote consequences. It is advisable to conduct a test with the forced rear bending of the foot in the patient's position lying on the back or standing. In this case, there is an occurrence of pain and discrepancy of bertov bones.
Radiographic changes in damage to the bonds of ankle
To assess the damage to the ankle joint, snapshots are always performed in standard projections, while X-ray finds can be very unexpected. If a tear-off, oblique or spiral fracture is detected in standard images, as well as a transverse or a diaphysic fracture in the distal bone, then there is also a gap of the corresponding ligaments. In such cases, there is no need to carry out an x-ray study of the ankle joint with a forced change in the position of the foot. However, such a study is shown in suspected instability or with its X-ray detection on the asymmetricness of the articular line and on other features.
The sign of the mixture of the bone of the kepent in the early stages can be determined with a radiographic or x-ray examination. There are certain difficulties in establishing landmarks that make it possible to identify the mixture of the tone of the bone. Although different authors use different corrective points, it is believed that its mixing of the kpeed relative to the rear edge of the heel bone by more than 3 mm is significant. The offset of more than 1 cm serves as an unconditional indication to the right. In the case of any doubt, a comparative study is carried out to obtain X-ray of contralateral ankle joint in similar projections and positions, provided that this joint was not injured in the past.
The test with the determination of the mixing of the tone of the bone during damage to the medial or lateral ligament system is also not too sensitive due to the variability of the displacement of the tone of the bone in healthy people and even in two normal ankle joints in one person. In addition, pain, spasm and edema can prevent adequate assessment of the joint condition. In addition, the efforts attached by the doctor during this test, as when testing with the front displacement, cannot be standardized. However, if the displacement of the tone bone exceeds 5 °, then the test can be considered positive. If the displacement is more than 25 °, the pathology definitely takes place. The difference in the mixing of the tank of 5-10 ° in damaged and intact joints is likely to be significant in most cases.
Arthritography of the ankle joint when conducting an experienced specialist is performed simply and quickly. The study must be carried out within 24-48 hours, since later the formation of bunches can prevent the output of a contrast substance from the joint cavity. Finding the contrast outside the joint usually indicates a gap. However, in healthy people, filling with a contrasting agent of tendon vagina of long finger bends and thumbs is observed in 20% of cases, the vagina of small-terber muscles is in 14% of cases, and the filling of the space of the tranny-heel joint is 10%. Assessment of the state of the heal and mulberry bundle with standard arthrographic methods is related to the high frequency of lies of non-negative results.
Classification of damage to ligaments
Allocate three degrees of damage to ligaments. Damage to the first degree is a stretching or microscopic bundles, causing local pain and minimal edema. In this case, the load is completely tolerated, and on radiographs there are no deviations from the norm.
In case of damage to the second degree, severe stretching and partial bundle breaks are observed, which cause significant soreness, moderate swelling and moderate pain during load. Radiographs in standard projections are uninformative. However, when the position of the foot changes, the loss of the ligament function is detected, which is determined by the abnormal ratio of the tanny bone and the joint fork.
The third degree of damage is set with full breakdowns. The patient is unable to transfer the load; There is a pronounced pain and swelling, and sometimes the deformation of the joint. On standard radiographs, a violation of the tanning of the tank and the articular plug is detected. Snapshots performed during the load on the joint are usually not required, but if there is a complete break, they are almost always positive if testing is carried out correctly.
The problem of treating damage to the ankle joint is widely discussed. Damage to the first degree ligaments can be treated with a tight bandage, an elevated position of limb and laying ice. Ice applique for 15 minutes causes local anesthesia, allowing you to perform a number of movements in the joint, after exercise, the ice is again superimposed for 15 minutes. Such appliques are prescribed to four times a day until the patient has a painless normal function in the joint. The load decision is made individually. In case of damage to the first degree ligaments in athletes, the complete resumption of the usual activity is not allowed until the victim can make a short run, not inhabit, run at normal speed in a circle or figure tracks in the form of eight, not feeling pain, and finally It will be able to bend a foot at a right angle without experiencing pain.
Damage to the second degree bundles is best treated with cold appliqués according to the technique described above and immobilization. In the case of extensive edema of Longets, crutches, ice laying and the corresponding positioning of the limb are used until edema falling; Then it is usually recommended to immobilize Longeta for walking for a period of 2 weeks with the subsequent 2-week use of hinged Longets.
Treatment of damage to third degree ligaments. The question of conservative or operational treatment should be solved individually with the participation of specialists. It is necessary to conduct a number of consultations with a traumatologist; This will provide appropriate diagnostics and proper treatment and prevent adverse remote effects of injury.
Groups have more significantly increased the pace of steps and the estimated speed of walking. All this indicates that the level of physical fitness of patients achieved as a result of physical rehabilitation after the treatment of ankle holenostic junction contributed to the acquisition of more sustainable walking skills. In general, at the end of the pedagogical experiment, 7 patients of the Econtrol Group went ...
The presence of parallel articular shelted and smooth bone surfaces forming the joint. This is achieved by immobilization or surgical correction. In most cases, damage to the ankle joint is well amenable to conservative treatment. The initial indication for surgical treatment is the impossibility of holding the tanny bone in an anatomically correct position in relation to ...
To the limb. We recommend wearing orthopedic shoes and elastic bandage. Disability is usually restored in 5-6 months. Treatment of freshly damage to the ankle joint with the use of skeletal extract. The skeletal stretch is treated with the fractures of ankle with a large displacement of fragments and edema, under which the induced reposition fails, and the operation is interfere with the operational treatment ...


Chapter 3. The role and means of adaptive physical culture in the treatment of injuries and damage to the ankle joint 3.1 Characteristics of adaptive-physical rehabilitation during fractures of the ankle bones of the tibia So, what is the role of adaptive physical education when the ankle rehabilitation is rehabilitated. First of all, you should figure out. What is an adaptive physical education. Adaptively Physical ...
Diagnostic tactics. Anamnesis .. The history is important not only complaints of the current moment, but also those that have already disappeared. It is necessary to identify all previous diseases, including operations, injuries and mental deviations .. There may be essentials such details like family anamnesis, data on vaccination and reception of drugs, professional anamnesis, refinement of the travel route, data on the sexual partner, the presence surrounded by animals. Physical research ...
Anamnesis . Seduced family anamnesis For anemia, any manifestations of liver diseases and biliary tract. Contact with patients with infectious hepatitis, staying in endemic to hepatitis regions during the last 2 months, parenteral interventions, drug administration, random sexual bonds over the last 6 months. Work with hepatotoxic substances. Alcohol abuse. Treatment with hepatotoxic drugs. Handic colic ...
Patomorphology. The spleen is increased, full. The vessels of the portal system and spleen are enlarged, sore, they can be aneurysms, hemorrhages, intricate clomes. Changes in the liver depend on the cause of PG. Varicose veins of the veins of the esophagus, stomach, rectum. Anamnesis . The presence of cirrhosis or chronic hepatitis. An indication of gastrointestinal bleeding in history. Instructions for alcohol abuse, blood transfusions, viral hepatitis B, with ...
True conjugate is less than 6.5 cm. Vaginal delivery is impossible even with the use of a fertilizing operation. Diagnostics. Anamnesis: Infantilism, transferred diseases and injuries, obstetric anamnesis . Objective study: general inspection, height 150 cm and below, assessment of Mikhaelis rhombus, spinal curvature, joint mobility; Schoomed belly in repeated and pointed - at first-night.
Huntington Korea (Khuene Dementia) is a hereditary disease. Khoneic hyperkinesis appear aged 30-40 years, later joins the progressive dementia, reaching the full decay of the person. When differentiation with senile choirs, family-owned anamnesis; At the beginning of the disease, the diagnosis facilitates the purpose of the L-dof, leading to a sharp increase in hyperkinesov.
Etiology. The overwhelming majority of cases (more than 95%) rheumatic etiology. External rheumatic anamnesis It is possible to assemble in 50-60% of patients. Almost always debuting until the age of 20, after 10-30 years, the vice becomes clinically pronounced. Irrevimatic cases of vice include heavy calcine sash and mitral valve rings, congenital anomalies (for example, Lutembash syndrome - 0.4% of all VPS), neoplasms and blood closures in the field of mitral valve and ...
Risk factors. Gluten enteropathy. Family anamnesis Herpetyiform dermatitis. Oncological diseases. Insolation. Clinical picture. Skin Changes .. True polymorphic rash: Ultimate, erythematous elements, stressful bubbles on an erythematometous background (may occur on unchanged skin) with a pronounced tendency to group and herpetiform location .. Tire bubbles dense, the contents first serous, then purre ...
Anamnesis . Contact with SI patients (hospital patients or care personnel with inflammatory changes on the skin, mucous membranes or other organs of definitely or presumably staphylococcal etiology) 1-10 days prior to the present disease. Eating infected in staphylococcus food. The development of a purulent inflammatory disease in a hospital, more often after 3 days from the moment of hospitalization. Surgical intervention with ...
Clinical picture. Anamnesis. Chronic gastric and duodenal diseases, liver, blood. Complaints of weakness, dizziness, drowsiness, faint, thirst, vomiting with fresh blood or coffee grounding, a party-shaped chair. Objective data. The pallor of the skin and visible mucous membranes, a dry language, a frequent and soft pulse, the blood pressure with a slight blood loss at first elevated, then normal.
in subepicardial, which can lead to the development of secondary them. The mechanism of the head of the heart wall with a stupid injury is a sharp increase in pressure in the heart chambers at its front-rear compression or a sharp blood flow from the bottom hollow vein during the safety belt injury. Clinical picture and diagnostics. . Complaints I. anamnesis .. Major complaints with heart injury - Pain in the chest, shortness of breath and interruptions in the work of the heart .. Often numerous complaints ...
Anamnesis. An indication of consumption of thermally untreated products, home-made food products and preserved in anaerobic conditions, mostly vegetables and mushrooms, as well as sausages, ham, smoked and salted fish, contaminated by bacteria. With wounded botulism - obtaining ribbons or accelerated wounds with significant tissue necrotic. Periods of the disease. Incubation, duration from 2 h to 7 days (rare up to 14 days).
. The acute form of Hirschprung's disease is manifested in newborns in the form of low congenital intestinal obstruction. Anamnesis . For Hirschprung's disease, in contrast to other forms of megacolon (tumor, megolone, on the background of atonic constipation in the elderly, toxic megalolon with non-specific ulcerative colitis), the appearance of constipation from birth or early childhood is characteristic. Often, parents note the presence of endocrine, mental and neurological deviations.
The infection of HSV-1 in persons over 4 years old in a population of more than 80% (European countries and the USA). Anamnesis . Contact with a patient with a clinically manifest form of herpetic infection over the past 2 weeks. If perinatal infection is suspected - information about the presence of a pregnant herpetic infection in various clinical form (incl. Latent). Classification. Localized form. Disseminated form. Latent shape. Clinical picture.
Clinical picture. Anamnesis. Contact with a sick chickenpox or hailing deprive for 11-21 days before the disease; Direct contact is optional. . Periods of the disease .. The duration of the incubation period is 11-21 days. Promotional period (optional) - up to 1 day .. period of rash (basic clinical manifestations) - 4-7 days .. reconstruction period - 1-2 weeks. . Clinical Symptoms .. Inxication Syndrome: Usually 3-5-day fever with ...
Diagnostics. Anamnesis . Study of field fields. Study of visual acuity. Ophthalmoscopy. The treatment is etiotropic. The course and forecast. With a stagnation disk, normal visual functions remain with a pronounced edema. In the future, there is a narrowing of the fields of view.
Classification. Latent (subclinical) form. Congenital form .. Acute form .. Chronic form. Acquired form. Anamnesis . An indication of a possible infection (the fact of infection of the mother in laboratory data, non-leaching of pregnancy, the birth of the dead fetus, hemotransphus and parenteral interventions in the past, sexual and / or close household contact with infected or patients, organ transplantation and tissues). The presence of possible primary manifestations ...
Differential diagnosis. Great importance is carefully assembled anamnesis, establishing the possibility of professional or household intoxication, accounting for the epidemiological situation in the identification of the nature and causes of the disease. In obscure cases, first of all, you should think about viral hepatitis. The identification of the so-called Australian antigen is characteristic of serum hepatitis B (it is also detected in viruses, rarely with other diseases).
Diagnostics. Anamnesis life (obstetric and postnatal) is the course of pregnancy, toxicosis, mothers disease; the flow rate, the duration of anhydrous interval, the use of obstetric benefits; Monthly weight gain of the child's body, transferred diseases in the early neonatal period. Social anamnesis (housing conditions, socio-economic condition of the family). Hereditary anamnesis - exchange, endocrine diseases, enzymopathy among family members ...
The clinical picture of the primary septic or primary pulmonary form is not fundamentally different from secondary forms, but the primary forms often have a shorter incubation period - a few hours. Diagnosis. The most important role in diagnostics in modern conditions is played by epidemiological anamnesis. Arrival from zones, endemic by plague (Vietnam, Burma, Bolivia, Ecuador, Turkmenistan, Karakalpak ASSR, etc.), or from the patient's anticipated stations with the described above ...
Anamnesis: Contact with patient polio for 3 weeks before the appearance of the first symptoms of the disease, staying in the region, dysfoliage in the incidence of poliomyelitis. The fact of vaccination of a live polio vaccine per month before the first symptoms of the disease or contact with vaccinated over the past two months (situations associated with the vaccine-based form of the disease).
History of the disease (Anamnesis Morbi)
Carefully and competently assembled history together with the clarified patient complaints is the basis for further medical diagnostic search. It is known that the one who asks well, correctly determines the diagnosis. "The art of the history of the history lies in the skillful rejection of the whole false, secondary and allocation of reliable facts that contribute to the correct diagnosis establishment" (R. R. is harmful, 1938). At the same time, the doctor is not the investigator and cannot insist on obtaining data that the victim wants to hide. Anamnesis is assembled solely in order to maximize medical care.
Attention should be paid to the following aspects:
1. What and where did it happen? The circumstances of the injury largely determine the direction of diagnostic search. At the same time, finding out the circumstances of injury, as well as the volume and content of the first
aid, the nature of immobilization of the limb and the peculiarities of transporting a patient to the medical institution have not only medical, but also legal significance. All of these data obtained from the words of the victim or from individuals who are accompanied are recorded in the history of the disease. Information reported by the doctor about production injury, road accident and numbers of cars at a road accident service, names or signs of people who have caused injury, is sometimes very important when determining the responsibility of officials or individual citizens and the appointment of material assistance to the victim. The collection of such information and its fixation in medical documents is the responsibility of medical personnel, to fulfill which it is necessary to relate to.
2. How did damage come? Finding out the injury mechanism and the duration of the post-traumatic period determine the tactics of the patient's survey. The doctor has the opportunity to familiarize himself in detail how the victim fell that he felt he could rise on his own. If the victim, the victim should be paid attention to the power of the traumatic effect, the patient's position at the time of injury, the condition of his psyche and consciousness after injury; There was a direct or indirect injury.
There are a number of typical injury mechanisms, on the basis of which one or another damage can be suspected, often encountered. Almost every anatomical region of the musculoskeletal system has its own standard injury mechanism. Knowledge of typical trauma mechanisms allows you to correctly orient the diagnostic search and avoid many errors.
3. date and the time of injury. Knowledge of the term that has passed since damage can greatly facilitate the diagnosis and development of therapeutic tactics. Thus, information on the fact that the expressed swelling of the foot "Lightning" developed, for half an hour after injury, or gradually increased during the week, already allowing the gravity of damage. For a long time (more than two weeks), which has passed since damage, significantly affects, for example, to assess the possibility of closed reposition of dislocation, the reposition of fractures, the implementation of the primary seam of nerves and tendons.
4. The nature of the previous medical care or treatment provided. Providing (or failure to provide) medical care to the victim in the first minutes and hours after injury significantly affects the clinical picture. When providing inadequate or first aid delay, symptoms already associated with the development of early complications - disorders of peripheral blood supply and innervation due to the compression of an incorrectly superimposed tire, bandage, the formation of epidermal bubbles (flicen) due to edema, which increases bone skin perforation Frances in the insolvency of immobilization and others. Timely dislocation controls, the exact reposition of bone fragments can significantly change the nature of the patient's complaints, reduce or reduce almost no intensity of pain.
It is important to make a complete picture of how the patient was treated earlier to preserve the sequence of treatment or to conduct its correction.
History ANAMNESIS VITAE)
Traditionally, the required data collected regardless of the nature of the pathology (date of birth, development, transferred diseases, allergic history, bad habits, working conditions and life, etc.).
At the same time, when examining patients of orthopedian traumatological profile, special attention should be paid:
The state of health and illness, leads or can lead to disabilities and changes in reparative ability (diabetes mellitus, thyrotoxicosis, collagenosis, tuberculosis, hormone therapy, climax, pregnancy, professional harm)
Harmful habits (especially systematic use of alcohol, narcotic substances) are able to lead to the development of osteoporosis, mental and neurological disorders and the like;
Previously suffered injuries, their consequences, functional results after the end of treatment;
Working conditions and life (sports) related to obtaining microtrams, elevated or significantly reduced physical and functional loads on the musculoskeletal system;
On allergic reactions caused by common and local analgesics, antibiotics (as medicines, most often used in traumatologists), as well as skin diseases (eczema, contact dermatitis);
Transferred operations, hemotransphus;
Tuberculosis, viral hepatitis, HIV infection.
Labor history - if the patient is disabled, he needs to issue a sick leave; If it continued to be disabled, the duration of the hospital sheet, the change in the conditions of work due to injury or the availability of disabilities is noted. It is also important to find out also the social status of the patient, on whom the informed cooperation of the patient with the doctor in the process of treatment, motivation is restored or the preservation of health and quality of life. It is desirable to explore the medical documents in the patient about the suffering diseases and operations.
Patient status (Status Praesens)
General Overview and Physical Inspection At the beginning of the review, it should be noted the peculiarities of the behavior of the patient, its appearance, the expression of the face, the gait, figure, the proportion of the body. Rate:
General (satisfactory, moderate gravity, heavy, terminal)
The level of consciousness and degree of mental adequacy (pay attention to possible narcotic or alcohol intoxication - with suspected such position, the appropriate clinical and laboratory survey is carried out and the act) is issued)
Body nature and body weight features (normostic, asthenic, hypersthenic type, cachexia, obesity);
Description of systems for systems (leather and subcutaneous tissue, breathing, blood circulation, digestion, urinary, endocrine, nervous system).
When damaged by any of the listed systems, its description is made in the description of the damage (Status Localis).
Inspection and examination of the place of damage (Status Localis)
Careful and system review helps to avoid many diagnostic errors. As a general type and position of the patient, the expression of his face, the colors of the skin can be estimated the severity of the general state of the patient and the preferential localization of the focus of pathology. According to a typical position, the characteristic position of the limb, an experienced doctor can diagnose "from one glance." But this does not exclude the need for a full-fledged survey. The passive position of the limb can be a consequence of a slaughter, fracture, paresis, paralysis. The forced position is observed with a pronounced pain syndrome (gentle installation) in the fracture area, the focus of inflammation, with violations of mobility in the joints (dislocation, contracture), as a result of compensation for the shortening of the limb (skew pelvis, scoliosis).
In case of inspection, impaired form and contours of the limbs, joints and body parts. Violation of the axis of the limb segment, angular and rotational deformation indicate a fracture. A patient with a "acute injury" can be inspected in the standing position, sitting or lying, depending on the nature of the injury obtained and its general state. Be sure to compare the symmetric portions of the body and limbs. The review can be considered full, if it is carried out with the patient's full exposure.
The position of the patient or damaged segment at the time of the inspection can be active, passive or forced. The active position indicates, as a rule, about relative well-being, when damage has not significantly affected the functions of the musculoskeletal system. Passive position means complete immobility and most often indicates a severe lesion of the brain (coma) or spinal cord (paralysis). The passive position of the individual segment is so characteristic that it is considered, as a rule, in a number of typical symptoms of one or another damage (for example, the passive position of the foot during damage to the small-terrestrial nerve - "horse stop"). The forced position of the entire body or a separate segment of the patient takes consciously or Unconsciously to reduce or stop pain.
There are a forced position that can be caused:
Painful syndrome - "sparing installation" (for example, the position of the upper limb when the shoulder dislocation, a semi-dying position and limitations of the chest excursion during rib fractures)
Morphological changes in the tissues (contractures, incorrectly fragile fractures, large skin scars)
With compensatory and pathological plants, which often turn out to be far from the affected area (hyperlordosis of the lumbar spine with a bent contract of the hip joint, skew the pelvis with the incorrectly thorough fracture of the bones of the leg).
Examination of the skin is carried out compared to intact parts of the body, paying attention to the presence of damage (wounds, abrasions, ulcers, fistulas, scars, epidermal bubbles, traumatic skin detachment), bruises (for example, para-hematoma can appear in severe acceleracy injury, hematoma In the crotch area - in case of damage to the pelvis), rashes on the skin (for example, phetechially rashes at fat embolism, asymmetry of the skin folds.
Under some bone fractures, especially superficially located, the prevalence and localization of hemorrhage are such typical that they can almost accurately establish a fracture character.
Palpation is a very important and informative method of examination. It is carried out with all the brush, the tips of the fingers of one or both brushes, the tip of one finger. Particular attention should be paid to the presence of palpation pain. In some cases, it is palpactorically pain that makes it possible to determine the localization of damage during clinical inspection. The pain can be local or spilled, sharply pronounced or insignificant, permanent or related to a certain position of the body or segment. With the help of palpation in some cases, it is possible to determine the presence of bone fragments under the skin, the nature of their displacement, the presence of pathological mobility, monitor the reproduction efficiency. On the displacement of individual bone protrusions or articular ends, it is possible to solve the question of the presence and nature of bone displacements, is not determined when inspection and does not palpate through its deep position. The presence of local bone pain after injury makes the doctor suspect a fracture even in the absence of radiographic data. Palpation of joints and paraarticular tissues makes it possible to determine the presence of fluid (hydraartrosis), to identify the change in the joint contours and the relationship between anatomical landmarks.
Information about the introduction of painkillers in the prehospital stage is also important.
Of great importance is the identification of attitudes, the nature and intensity of which is significantly different in different states.
The causes of crepitiation may be:
Friction of bone fragments between themselves for fractures;
Inflammatory and scar changes in tendon vagina and articular bags (tendovaginitis, bursitis)
Deforming arthrosis of the joints, the presence of intra-joint lesions and foreign bodies;
The presence of air in the subcutaneous tissue is subcutaneous emphysema (chest injury with lung damage, gas gangrene).
Reducing or lack of transmission of percussion sound on the phonedoscope with auscultation and percussion on the bone may indicate a fracture. However, with the advent of modern highly informative research methods (primarily radiological), auscultation and percussion in the diagnosis of fractures are used very limited. These methods are extremely important for the diagnosis of the complications of hemopneumothrax, pneumonia, the presence of free fluid in the abdominal cavity, etc.
Clinical signs of fractures. There are reliable (absolute) and indirect (relative) signs of bone fractures, which are determined by the doctor with a clinical examination of the victim.
Significant (absolute) includes signs characteristic only for fractures that cannot be marked without it:
Pathological mobility of fragments in the area of \u200b\u200balleged damage;
Bone fragments attitudes;
Pathological deformation of the axis of the long tubular bone with a change in its length;
Palpation of bone fragments under the skin;
Stretching bone fragments in wound with open fractures.
The presence of at least one reliable (absolute) signs are sufficient to confirm the diagnosis of the fracture. It should be remembered that the artificialization of pathological mobility, bone fragments attachment can be added to the fabrics, increase pain, cause a number of heavy complications - damage to peripheral vessels and nerves. Therefore, such symptoms can only manifest themselves in the patient's examination process in a state of fainting,
printing or when overlaying transport tires and transportation. Specifically cause symptoms of attitudes, pathological mobility of bone fragments in order to establish a diagnosis unacceptable!
Indirect (relative) features can be caused not only by a fracture, but also by other damage or diseases.
The diagnosis of a fracture can only be delivered on the basis of a combination of several indirect (relative) signs of fractures, which are found to meet:
Local pain (at rest, with movements or functional load, with palpation or percussion)
Violation of the function;
Changing the contours of the segment, swelling of soft tissues (swelling), a change in the skin color, local hyperthermia, the presence of epidermal bubbles (flicten)
Availability of wounds, abrasion, bruises, subcutaneous and intradermal hematomas;
Peripheral circulation and innervation disorders;
The asymmetry of the body (may be associated not only with damage, but also with pain pathological installation).
The symptom of the axial load (local pain in the zone of the intended fracture at a light load directed along the axis of the bone), although it occurs most often during fractures, also refers to indirect features, because it may also be found at local pathological processes (tumor, osteomyelitis).
When dislocation and erasevivihs (combinations of a dislocation of dislocation) in the joints, symptoms of elastic resistance can be determined in the joint attempts in the joint, the cluster of the fluid in the joint cavity (hydraartrosis, hemartroprosis), as well as the violation of the symmetry of external benchmarks.
For each location of damage, there are characteristic symptoms that will be described in the appropriate sections of the textbook. At the same time, the following techniques are used: evaluation of the stroke, anatomical circuits, palpation, percussion, auscultation, study of peripheral blood supply and innervation of limbs, determination of deformations and amplitude of movements in the joints.
What else to read
THE LAST NOTES
- Common Massage Procedure Description
- Effective cellulite treatment at home
- The history of the appearance and distribution of kefir how to write a story about kefir
- Funds that will help cause disgust for alcohol how to cause alcohol disgust
- The history of the emergence and distribution of kefir who invented kefir
